Table of Contents
Google Analytics 4 brought a whole new way of tracking to many marketing specialists and web analytics users. Besides an updated dashboard, new metrics, and new dimensions, many have said GA4 ushers in a new era: a cookie-less future.
This claim can be a bit misconstrued, as Google Analytics 4 still uses cookies, but many of the cookies and tracking as we know it will soon fade by the wayside.
A crucial component of GA4’s tracking mechanism is the use of cookies. We’ll dive into how GA4 utilizes cookies to enhance website analytics.
1. Identifying Unique Users with _ga Cookie
First things first, how does GA4 identify unique users? It can’t simply bucket all users together, as this would make reporting completely useless.
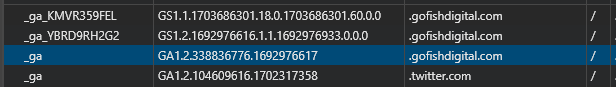
To identify unique users, GA4 sets a cookie named _ga.
This cookie is created when a user first visits a website and assigns a unique identifier. This identifier is essential for tracking the user’s future visits, allowing website owners to understand repeated interactions on their site.
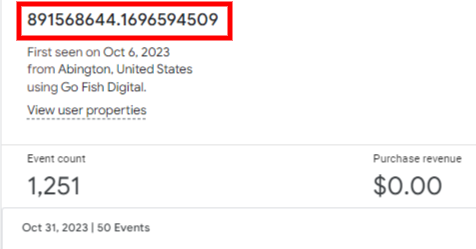
You can look into each user by using an exploration. This particular exploration is called the User Explorer.
While this User Explorer doesn’t contain the _ga, it does contain the full User ID.
You can look at this in real-time by inspecting the page element, going to application, and filtering down the cookies by _ga.
Users can still opt out of this cookie tracking if given the option on the website via a cookie consent banner.
2. Tracking User Sessions via _gid Cookie
One of the most significant changes in GA4 was how it tracked sessions and new metrics such as engagement time and engaged sessions.
For this, GA4 uses the _gid cookie. Sessions are the bread and butter of web analytics reporting, helping us view insights and overall traffic trends.
The _gid cookie, which expires after 24 hours or when the user closes their browser, is vital in monitoring these engagement periods.
Its other uses include:
- Pageview counting
- Distinguishing current users
- Session tracking
3. Enhancing Measurement with Advanced Features
GA4 goes beyond basic tracking with enhanced measurement features supported by cookies. These include cross-device tracking, enabling the monitoring of users across multiple devices (e.g., desktops, laptops, mobile phones), and user IDs, which link user behavior to specific accounts. These advanced features provide a more holistic view of user interactions.
Cross-device tracking is essential in today’s day and age. Rarely will one user stick to one device when visiting a website over time, often switching between a mobile and desktop device.
GA4’s cookies allow web analysts to track a user’s behavior over multiple devices, which helps us better understand the conversion path, attribution modeling, and overall user behavior.
These cookies also allow for more advanced analysis, such as a customer’s lifetime value, enhanced targeting, and predictive analytics.
4. Compliance with Privacy Regulations
Last but certainly not least is the pressure and necessity for GA4 to adhere to privacy regulations worldwide. GA4’s first-party cookies are more privacy-conscious than third-party cookies since they’re directly set by the website you are visiting.
On the other hand, third-party cookies are set from external websites and can track your activity throughout different parts of the web.
GA4 has also made sure to adhere to stricter privacy regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA).
Conclusion
GA4’s use of cookies is integral to offering a detailed and accurate understanding of website visitor behavior. GA4 is equipped to be the next analytics tool that will consider the average user’s privacy concerns.
If you’re looking for additional analytics help, feel free to reach out!
Search News Straight To Your Inbox
*Required
Join thousands of marketers to get the best search news in under 5 minutes. Get resources, tips and more with The Splash newsletter: